Supported rail joint: rail joint in which the rail ends rest on a single sleeper called "joint sleeper".
Suspended rail joint:the rail joints in which the rail ends are projected beyond sleepers are known as suspended rail joints
Bridge rail joint: joints in the rail ends are projected beyond sleepers and are carried by the flat or corrugated plate called bridge plates are known as bridge rail joint.
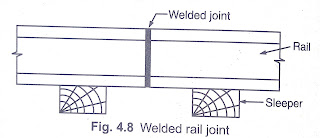
Welded rail joint: rail joint in which the rail ends are welded together are called rail joint
Square or even rail joint:when the joint of one rail of a track are directly opposite the joint of another rail they are known as square or even rail joint
Staggered or broken rail joint:in this the joint of one rail of a track are not directly opposite to the joint of other rail
Compromise rail joint:the rail joint where two different railway sections are required to be join together are known as compromise rail joint.





Comments
Post a Comment